With label skin diagram worksheet answers at the forefront, this article delves into the fascinating realm of skin anatomy and its multifaceted functions. From understanding the intricate layers of the skin to exploring the roles of different skin cells, this comprehensive guide unravels the complexities of our largest organ, providing valuable insights for a deeper understanding of skin health and well-being.
Throughout this exploration, we will uncover the protective barriers, thermoregulatory mechanisms, and sensory capabilities of the skin. By examining common skin disorders and delving into proper skincare practices, we aim to empower individuals with the knowledge and tools to maintain healthy, radiant skin.
Anatomy of the Skin
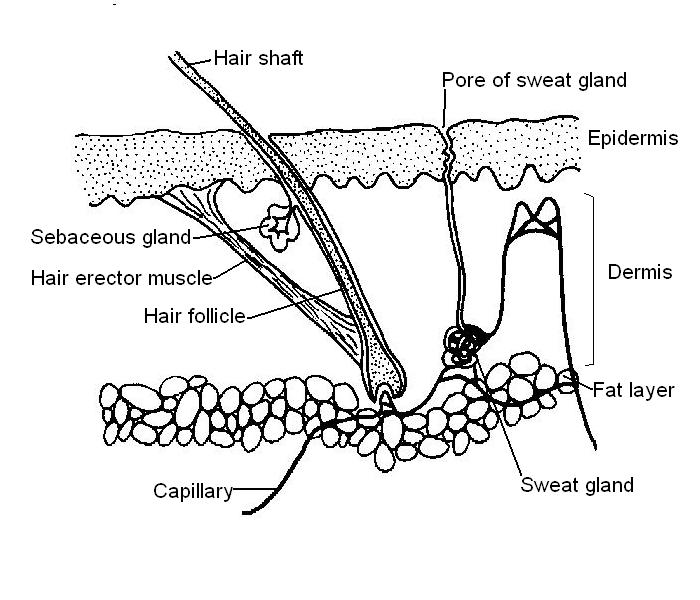
The skin, the body’s largest organ, is a complex and dynamic structure composed of multiple layers. Each layer plays a crucial role in protecting and maintaining the overall health of the body.
Layers of the Skin
- Epidermis:The outermost layer, composed of keratinized cells, provides a waterproof barrier against pathogens and environmental stressors.
- Dermis:The middle layer, containing connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves, provides strength and elasticity to the skin.
- Hypodermis:The innermost layer, consisting of fat cells, insulates the body and cushions it against external forces.
Skin Cells
The skin is composed of various types of cells, including:
- Keratinocytes:Produce keratin, a protein that forms the protective barrier of the epidermis.
- Melanocytes:Produce melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color and protects it from UV radiation.
- Langerhans cells:Immune cells that protect the skin from pathogens.
Functions of the Skin
The skin performs a multitude of essential functions, including:
Protective Functions
- Physical barrier:Protects against mechanical injury, UV radiation, and pathogens.
- Chemical barrier:Prevents the absorption of harmful substances.
- Immunological barrier:Contains immune cells that fight infections.
Regulation of Body Temperature, Label skin diagram worksheet answers
The skin helps regulate body temperature through:
- Vasodilation:Widening of blood vessels to increase heat dissipation.
- Vasoconstriction:Narrowing of blood vessels to reduce heat loss.
- Sweating:Evaporation of sweat cools the body.
Sensation and Absorption
The skin contains nerve endings that detect sensations such as touch, temperature, and pain. It also allows for the absorption of certain substances, such as oxygen and topical medications.
Skin Disorders
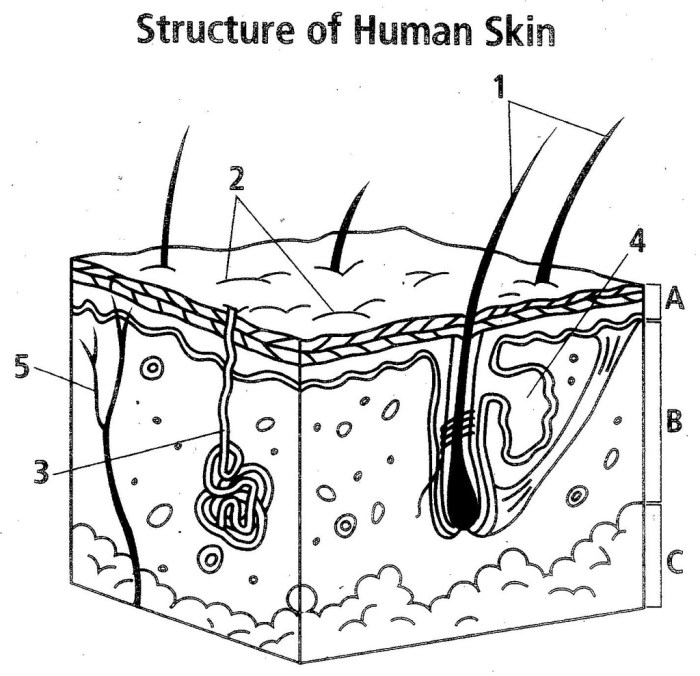
Various factors can cause skin disorders, including genetics, environmental factors, and infections.
Common Skin Disorders
- Acne:Inflammation of the hair follicles, leading to pimples and blackheads.
- Eczema:Dry, itchy skin caused by inflammation.
- Psoriasis:A chronic skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches.
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing skin disorders involves:
- Maintaining good hygiene:Regular bathing and using appropriate skincare products.
- Protecting from sun exposure:Using sunscreen and wearing protective clothing.
- Avoiding irritants:Identifying and avoiding substances that trigger skin reactions.
- Topical medications:Creams, ointments, and gels applied directly to the affected area.
- Oral medications:Antibiotics, anti-inflammatories, and immunosuppressants taken orally.
- Phototherapy:Exposure to ultraviolet light to reduce inflammation.
- Protects from damage:Prevents premature aging, sun damage, and environmental stressors.
- Maintains skin health:Keeps skin hydrated, supple, and free from blemishes.
- Boosts confidence:Improves skin appearance and self-esteem.
- Cleansers:Remove dirt, oil, and makeup from the skin.
- Moisturizers:Hydrate and soften the skin.
- Sunscreen:Protects from UV radiation.
- Anti-aging creams:Reduce wrinkles and fine lines.
- Cleanse:Twice daily, using a gentle cleanser suitable for your skin type.
- Moisturize:Apply a moisturizer after cleansing to keep skin hydrated.
- Protect from the sun:Wear sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher every day.
- Exfoliate:Remove dead skin cells with a gentle exfoliator once or twice a week.
- Use masks:Apply face masks to provide extra nourishment and hydration.
- Basal cell carcinoma:The most common type, usually appears as a pearly or waxy bump.
- Squamous cell carcinoma:Less common, presents as a red, scaly patch that may bleed or crust.
- Melanoma:The most serious type, appears as an irregular mole with changes in size, shape, or color.
- UV exposure:Excessive exposure to sunlight or tanning beds.
- Fair skin:People with fair skin are more susceptible to UV damage.
- Family history:Having a family member with skin cancer increases your risk.
Treatment options for skin disorders include:
Skin Care
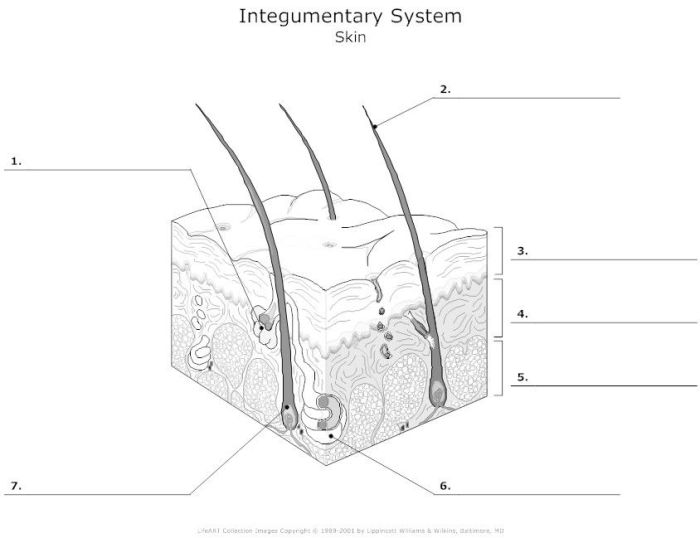
Proper skin care is essential for maintaining healthy, youthful-looking skin.
Importance of Skin Care
Skin Care Products
Skin care products include:
Healthy Skin Care Routine
Skin Cancer: Label Skin Diagram Worksheet Answers
Skin cancer is a common and potentially serious disease that develops when skin cells become damaged by UV radiation.
Types of Skin Cancer
Risk Factors
Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection and treatment are crucial for successful outcomes. Regular skin checks by a dermatologist are recommended for early detection.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the three main layers of the skin?
The three main layers of the skin are the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis.
What is the function of the epidermis?
The epidermis is the outermost layer of the skin and its primary function is to protect the body from external threats such as bacteria, viruses, and UV radiation.
What is the dermis?
The dermis is the middle layer of the skin and it provides strength and elasticity to the skin. It also contains blood vessels, nerves, and hair follicles.
What is the hypodermis?
The hypodermis is the innermost layer of the skin and it is made up of fat cells. It insulates the body and provides cushioning.