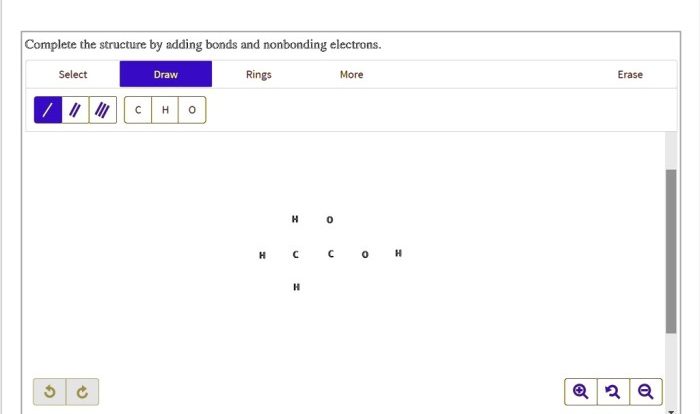
Consider the reaction of an alkyl bromide and hydroxide ion. – Nucleophilic substitution reactions, exemplified by the reaction between alkyl bromides and hydroxide ions, play a crucial role in organic synthesis. This reaction involves the replacement of a leaving group by a nucleophile, leading to the formation of a new carbon-heteroatom bond.
Understanding the mechanism, stereochemistry, and applications of this reaction is essential for comprehending the fundamental principles of organic chemistry.
Alkyl bromides serve as electrophiles in these reactions, while hydroxide ions act as nucleophiles. The rate of the reaction is influenced by various factors, including the nature of the alkyl group, the solvent, and the temperature. The reaction proceeds through a transition state, resulting in the formation of an alcohol as the product.
Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
Nucleophilic substitution reactions are a type of chemical reaction in which a nucleophile, a species with a lone pair of electrons, attacks an electrophile, a species with a positive charge or an electron-deficient atom, and replaces a leaving group.
In nucleophilic substitution reactions, alkyl bromides act as electrophiles due to the presence of a polar C-Br bond. The electrophilic carbon atom in the alkyl bromide is attacked by the nucleophile, resulting in the substitution of the bromide ion with the nucleophile.
Factors Affecting the Rate of Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
- Nucleophile strength:Stronger nucleophiles react faster.
- Electrophile reactivity:More reactive electrophiles react faster.
- Solvent polarity:Polar solvents favor nucleophilic substitution reactions.
- Temperature:Higher temperatures increase the rate of reaction.
Reaction of Alkyl Bromides with Hydroxide Ion
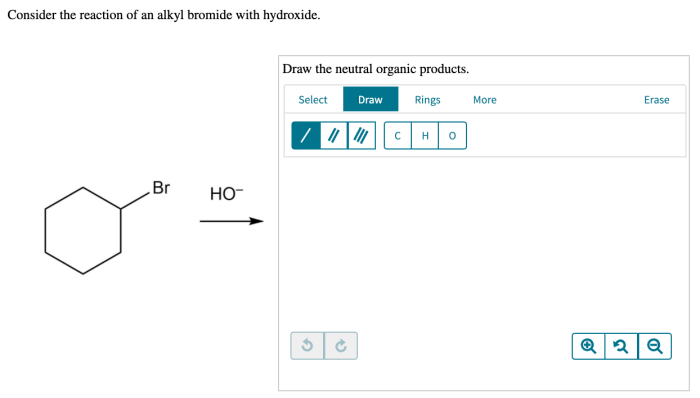
The reaction of an alkyl bromide with hydroxide ion is a classic example of a nucleophilic substitution reaction. In this reaction, the hydroxide ion acts as the nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon atom in the alkyl bromide.
Mechanism
The reaction proceeds via a two-step mechanism:
- Nucleophilic attack:The hydroxide ion attacks the electrophilic carbon atom in the alkyl bromide, forming a tetrahedral intermediate.
- Departure of the leaving group:The bromide ion is expelled from the intermediate, resulting in the formation of the product, an alcohol.
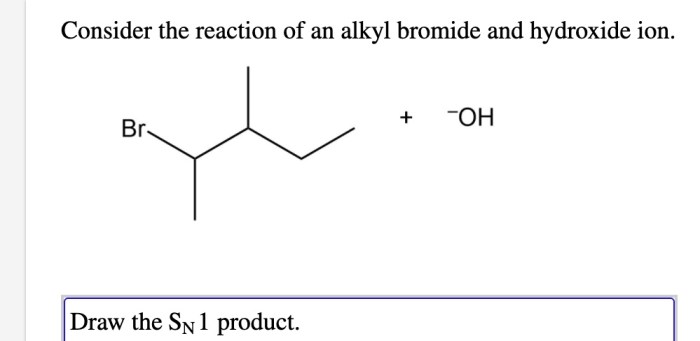
Stereochemistry of the Reaction: Consider The Reaction Of An Alkyl Bromide And Hydroxide Ion.
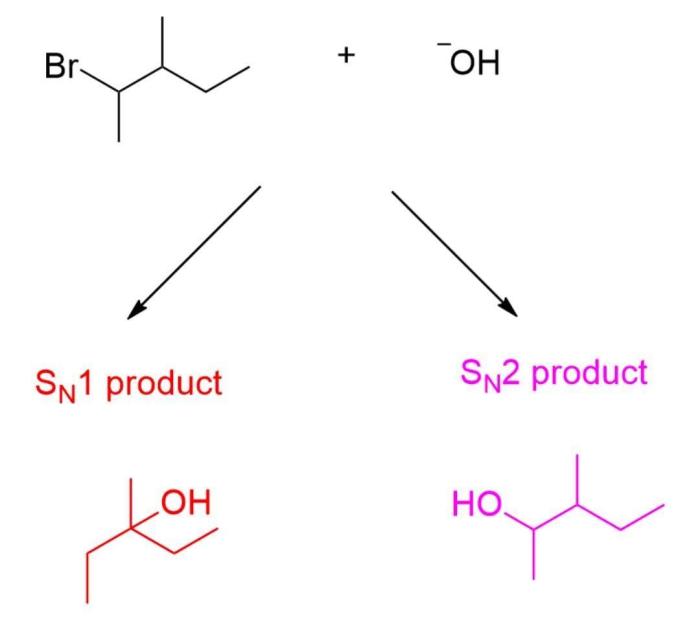
The stereochemistry of the reaction of alkyl bromides with hydroxide ion depends on the mechanism of the reaction.
SN2 Reactions
In SN2 reactions, the nucleophile attacks the electrophilic carbon atom from the opposite side of the leaving group, resulting in an inversion of configuration.
SN1 Reactions, Consider the reaction of an alkyl bromide and hydroxide ion.
In SN1 reactions, the leaving group departs first, forming a carbocation intermediate. The nucleophile can then attack the carbocation from either side, resulting in a racemic mixture of products.
Applications of the Reaction
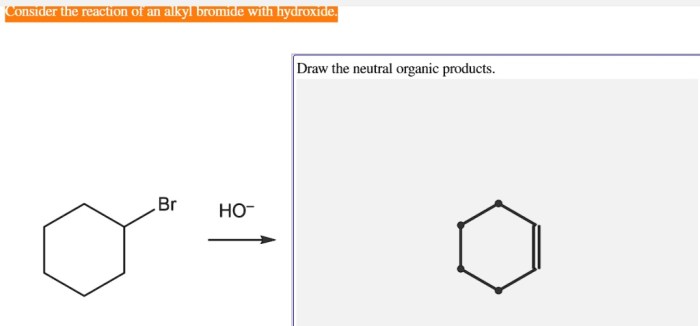
The reaction of alkyl bromides with hydroxide ion is a versatile reaction that is used in a variety of organic synthesis applications.
- Alkylation of alcohols:Alkyl bromides can be used to alkylate alcohols, producing ethers.
- Synthesis of alkenes:Alkyl bromides can be used to synthesize alkenes via elimination reactions.
- Synthesis of alkynes:Alkyl bromides can be used to synthesize alkynes via dehydrohalogenation reactions.
However, this reaction has some limitations. For example, it is not suitable for the synthesis of tertiary alcohols due to the formation of carbocations, which can undergo rearrangements.
Alternative methods for nucleophilic substitution include the use of Grignard reagents, organolithium reagents, and alkoxides.
FAQ Guide
What is the mechanism of the reaction between alkyl bromides and hydroxide ions?
The reaction proceeds through a nucleophilic substitution mechanism, involving the attack of the hydroxide ion on the electrophilic carbon of the alkyl bromide, leading to the formation of an alcohol and bromide ion.
What factors affect the rate of the reaction?
The rate of the reaction is influenced by the nature of the alkyl group (primary, secondary, or tertiary), the solvent polarity, and the temperature.
What are the applications of the reaction of alkyl bromides with hydroxide ions?
This reaction is widely used in organic synthesis for the preparation of alcohols, ethers, and other organic compounds.